ยาลดความดันในกลุ่ม calcium channel blocker ทำงานโดยความรู้ที่ว่า ca2+ นั้นใช้ในการหดตัวตัวของกล้ามเนื้อดังนั้นเมื่อไป block มันแล้วก็จะทำให้ให้กล้ามเนื้อหดตัวได้น้อยลง จึงก่อให้เกิด vasodilatation ของ vessel และลดความแรงในการหดตัวของกล้ามเนื้อหัวใจ (negative ionotropic) ซึ่งต่างกับกลุ่ม beta channel blocker ที่ไปปิดกั้นที่สัญญาณไฟฟ้าที่ส่งมาที่หัวใจแต่ว่าความแรงในการบีบตัวของกล้ามเนื้อนั้นยังเท่าเดิม จากความรู้ที่กล่าวมาข้างต้นทำให้ผู้ป่วยที่ทานยา CCB มีผลข้างเคียงอย่างหนึ่งคือ tachycardia จากการที่ BP drop จากแรงบีบตัวของกล้ามเนื้อหัวใจที่ลดลง ทำให้ barorecepter ส่งสัญญาณกลับไปให้เพิ่มอัตราการเต้นของหัวใจ
จากความรู้เรื่อง action potential ใน cardiac muscle ทำให้รูได้ว่า mechanism อีกอย่างหนึ่งของ CCB คือจะยั้บยั้งการนำกระแสไฟฟ้าในหัวใจได้เช่นกัน ดังนั้นก็ทำให้มีโอกาสเกิด heart block ได้คล้ายๆกับ beta channel blocker โดยยากลุ่ม beta channel blocker นั้นจะ titrate ให้ได้ heart rate ที่ต้องการได้ง่ายกว่ากลุ่ม CCB
ยา CCB แบ่งเป็นอีก 3 กลุ่มคือ Dihydropyridine (-dipine),Phenylalkylamine(-pamil),Benzothiazepine(Diltiazem)
โดยยากลุ่ม dihydropyridine นั้นจะมีผลต่อ vessel มากกว่า ส่วนกลุ่ม phenylalkylamine จะมีผลต่อกล้ามเนื้อหัวใจมากกว่า ดังนั้นมักใช้เป็นยาพวก anti-angina ด้วย ส่วนกลุ่ม Benzothiazepine นั้นออกฤทธิ์ทั้งแต่ vessel และ cardiac
19 August 2009
ยาลดความดันกลุ่ม calcium channel blocker
Hypertension and Stroke

จากกราฟจะเห็นว่ากระบวนการ autoregulation ของร่างกายอยู่ที่ mean arterial pressure ที่ 50-150 mmHg เมื่อไหร่ก็ตามถ้า MAP ลดลงต่ำกว่า 50 mmHg จะทำให้ Cerebral blod flow ที่ไปที่สมองไม่เพียงพอเกิดเป็น ischemic stroke ในทางกลับกันถ้า MAP > 150 ก็จะทำให้เกิด CBF ที่มากเกินไปเกิดเป็น hemorrhagic stroke ได้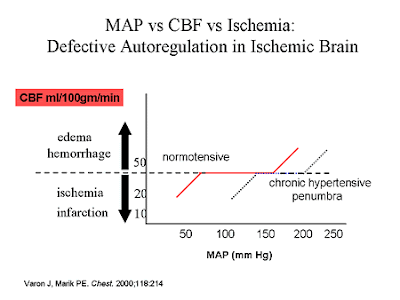
มาดูอีกกราฟหนึ่งในผู้ป่วยที่มี hypertension จะพบว่า autoregulation interval นั้นเปลี่ยนไป โดย interval ใหม่ที่เกิดขึ้นจะแคบกว่าในคนปกติ ในคนไข้ hypertension นั้นความดันจะ swing ได้ค่อนข้างง่ายอยู่แล้ว เพราะฉะนั้นถ้าในกรณีทำหัตถการที่ทำให้คนไข้เครียดหรือเจ็บปวดก็จะทำให้ BP สูงเกิด hemorrhagic stroke กลับกันในกรณีในคนไข้ที่ทำหัตถการภายใต้การวางยาสลบ ถ้าให้ deep sedation มากเกินไปหรือยานำสลบที่ลดความดันมากเกินไปก็ทำให้เกิด ischemic stroke ตามได้เช่นกัน
เพื่อความเข้าใจมากขึ้นเข้าไปอ่านประกอบได้ที่นี้ http://medinfo2.psu.ac.th/anesth/education/trauma2.html
Intracranial Pressure and Cerebral Blood Flow
The brain is only able to withstand very short periods of ischaemia, unlike the kidney, liver or muscle
Maintenance of cerebral blood flow depends on a balance between the pressure within the skull, intracranial pressure (ICP) and the arterial pressure of the blood, mean arterial pressure (MAP).
Thus when blood pressure falls, physiological mechanisms attempt to maintain flow to prevent ischaemia. This process is autoregulation
If there is an increase in the volume of either the brain or blood the normal initial response is a reduction in CSF volume within the skull. CSF is forced out into the spinal sac
It is believed that a MAP that is greater than 60 mmHg is enough to sustain the organs of the average person.
CPP = MAP - ICP (normal 10 mmHg)
Normal cerebral perfusion pressure is 80 mmHg
but when reduced to less than 50 mmHg there is metabolic evidence of ischaemia and reduced electrical activity
In the head injured patient, CPP should not fall below 70 mmHg.
Drowsy and confused: (GCS 13-15)ICP=20 mmHg,Severe brain swelling (GCS <8) ICP=30 mmHg
The normal cerebral blood flow is 45-50ml 100g-1 min-1, ranging from 20ml 100g-1 min-1 in white matter to 70ml 100g-1 min-1 in grey matter. There are two essential facts to understand about cerebral blood flow. Firstly, in normal circumstances when the flow falls to less than 18-20ml 100g-1 min-1, physiological electrical function of the cell begins to fail
Normally autoregulation maintains a constant blood flow between MAP 50 mmHg and 150 mmHg
Carbon dioxide causes cerebral vasodilation. As the arterial tension of CO2 rises, CBF increases and when it is reduced vasoconstriction is induced.
Full article here http://www.nda.ox.ac.uk/wfsa/html/u08/u08_013.htm
14 August 2009
IV anesthetic agent
ยานำสลบที่ให้ทางหลอดเลือดดำมีด้วยกันหลายตัว เราพอจะมีขอพิจารณาคร่าวๆในการเลือกใช้ดังนี้
- Thiopental ให้การนำสลบที่ค่อนข้าง smooth แต่อาจจะกระตุ้นให้เกิดการหลั่ง histamine ได้ thiopental มีฤทธิ์ vasodilatation แต่จะกระตุ้นให้ increase heart rate ทำให้ BP ไม่ drop มากนัก ถ้าให้ thiopental เป็นจำนวนมากจะทำให้ผู้ป่วยตื่นได้ช้า
- Propofol นำสลบได้เร็ว และหมดฤทธิ์เร็ว มีผลให้ BP drop เนื่องจากมีฤทธิ์ vasodilatation แต่ไม่ compensate ด้วยการเพิ่ม Heart rate และยังทำให้เกิด apnea ได้ค่อนข้างสูง (30%) เวลาฉีด propofol ยังแสบอีกด้วยแนะนำให้ฉีดเข้าเส้นเลือดดำที่ค่อนข้างใหญ่จะดีกว่า
- Ketamine มีฤทธิ์ในการนำสลบและ " แก้ปวด" ด้วย เหมาะในการนำสลบในคนไข้ที่อยู่ในภาวะ shock เพราะมีผลกระตุ้น ทั้ง HR และเพิ่ม muscle contraction ของหัวใจ ทำให้ BP สูง แต่การใช้ยานี้ทำให้เกิดลักษณะ dissociate anesthesia ได้
- Etomidatel BP ค่อนข้าง stable ไม่ทำให้เกิดการหลั่ง histamine มีอาการระคายเคืองเวลาให้ยาเช่นเดียวกับ propofol